Tips for Writing Learning Objectives
What are learning objectives?
- Learning objectives are specific, measurable, observable student behaviors;
- An objective is a description of a performance you want learners to be able to exhibit before you consider them competent; and
- Learning objectives can describe these behaviors at a course, module/unit, or session level.
Why have objectives?
- To convey instructional intent to students;
- To ensure that learning is focused clearly enough that both students and teacher know what is going on;
- To provide direction to instruction; and
- To provide guidelines for alignment of assessment.
How specific and detailed should objectives be? What are the components of a learning objective?
A common way of framing objective components is using the A-B-C-D model. These include: audience, behavior, condition, and degree.
- A (audience) – Who is the target audience? (e.g. “Students will…”)
- B (behavior) – What is the real work to be accomplished by the student? (e.g. “design”)
- They should be both observable and measurable behaviors.
- C (condition) – What are the conditions/constraints where the audience will be expected to perform these tasks within? (e.g. “given an amino acid sequence of a protein…”).
- D (degree) –How will the behavior need to be performed? (e.g. “the gene for expression of a protein”).
Examples:
- Students will be able to predict the net charge on ionizable groups at any given pH.
- Students will be able to predict, in qualitative terms, the role of molecular forces in stabilizing protein-drug complexes and the potential effect of chiral centers on drug activity.
- Given the target of a drug in polymer biosynthesis, students will be able to predict the effect of that drug on bacteria or viral growth.
- Students will describe past public policy debates in the United States that exemplify a broad range of historical and contemporary concerns and analyze them using a provided theoretical framework.
- Students will identify which patients will benefit from the pertussis vaccine based on their demographics and comorbidities
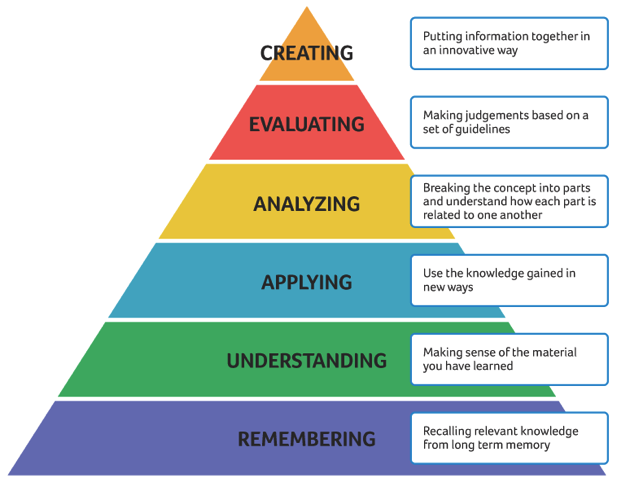
Writing Objectives Using Bloom’s Taxonomy and Associated Action Verbs
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a classification of different objectives. The taxonomy was proposed in 1956 by Benjamin Bloom but was recently updated. These 6 levels can be used to structure the learning objectives, lessons, and assessments of your course. The taxonomy ranges from the Remembering (Lowest cognitive task) to Creating (Highest cognitive task). Note: This taxonomy addresses the cognitive domain but other taxonomies are available for the psychomotor and affective domains.
It is important to remember that these verbs are not observable and therefore are not measurable:
- understand
- know
- grasp
- appreciate
Consider using the verbs below to define your objectives and the example activities to assess achievement of the learning objectives.
Please feel free to reach out to CETL (cetl@uconn.edu) if you would like further assistance on writing learning objectives and aligning them with your assessments.
| Measurable Action Verbs across Bloom’s Taxonomy for Writing Learning Objectives
“After successfully completing this course/ module, you will/ should be able to…” |
|||||
| Remembering | Understanding/ Comprehension | Applying | Analyzing | Evaluating | Creating/ Synthesis |
| gather & recall information | grasp meaning; explain, restate ideas | use learned material/ knowledge in a new situation | separate material into component parts; show
relationships between parts |
make choices; judge the worth of material against
stated criteria |
put together separate ideas to form new
whole; establish new relationships |
| define
identify describe label list name find state match select locate memorize recall reproduce tabulate tell copy discover duplicate enumerate listen omit read recite record repeat Activities: Read books, articles Watch video content Research Notes Label
|
explain describe interpret paraphrase summarize classify compare differentiate discuss extend associate contrast demonstrate express identify indicate infer relate restate select translate cite give examples of group illustrate order report represent research review rewrite showActivities: Analogy Outline Summary Graph Drawing, Diagram Collage Skit Speech Personal statement Collection
|
apply solveillustrate modify use calculate change choose demonstrate discover experiment relate show sketch complete construct interpret prepare produce report teach administer collect compute determine develop examine explain measure list operate practice record schedule transfer convert Activities: Demonstration, performance Solve Puzzle/ Problem Drawing, Diagram Map Journal Interview |
analyze
compare classify contrast distinguish infer separate explain select categorize connect differentiate discriminate divide order point out prioritize subdivide appraise break down conclude deduce devise diagram dissect estimate experiment illustrate organize outline plan question test Activities: Chart, graph Model Survey Break down an argument Syllogism Interpret different levels of meaning |
evaluate
justify recommend choose select distinguish estimate support defend compare decide discriminate predict rank score rate grade measure test conclude debate editorialize find errors convince Activities: Rubric Editorial Evaluation Recommendation Review Discussion |
create design composedevelop produce formulate devise write rearrange hypothesize predict Activities: Article, book Poem, song, media product Game Report Invention |
Note: Depending on the context, several of these Verbs/ Activities can be used at different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy. www.teachthought.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/verbs-for-blooms-taxonomy.jpg 1/1
Quick Links
![]()
Consult with our CETL Professionals
Consultation services are available to all UConn faculty at all campuses at no charge.